Editor’s Note: This entry is currently being researched for additional information. Please request editorship to improve the quality of this article.
About
3D Printing is the practice of creating objects from three-dimensional digital models. Online communities have arisen for 3D printing enthusiasts, including open-source databases where digital models can be downloaded, including Makerbot’s Thingiverse and Defense Distributed’s DEFCAD.
History
In 1983, Chuck Hull[2] invented the process known as stereolithography, which would create solid objects by “printing” thin layers of material on top of one another through lasers and ultraviolet light. Two years later, he founded the company 3D Systems[3] to manufacture 3D printers and other related technologies, specifically for industrial use. By 2000, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology began developing their own 3D printing process, using powders and a binding material.[4]
In 2005, RepRap[1] launched, dedicated to building a printer that would replicate itself. By 2006, the prototype Darwin (shown below, left) successfully printed its first piece. Two years later, personal 3D printers began to be developed by Desktop Factory (shown below, right), which began selling their models at $4995 each in 2007.[5]
In 2009, founding member of the RepRap foundation Zach “Hoeken” Smith, along with Bre Pettis and Adam Mayer, launched MakerBot Industries[6], featuring build-it-yourself printers. The company launched on March 15th, 2009[7], offering a kit containing the pieces to build their first printer model, the CupCake CNC, for $750. Approximately a month later, the laser-cut design files were made freely available on the Thingiverse[9], allowing anyone with access to a laser cutter to build their own MakerBot for free.
Online Presence
The 3D printing marketplace and community site ShapeWays[14] was launched on February 18th, 2008. In November of that year, MakerBot launched the Thingiverse[10] website, which served as repository of digital design files for users to share. The website contains designs licensed under the GNU General Public License and Creative Commons, which can be used in a variety of machines including 3D printers, laser cutters and milling machines. In 2010, Thingiverse won an honorable mention in the Digital Communities category at ARS Electronica.[11] On November 21st, 2011, the blog 3DPrinting[15] was launched, featuring news stories related to virtual design and fabrication.
Controversy
On June 4th, the organization Defense Distributed (DD) was founded by crypto-anarchist Cody Wilson to create an open-source plastic gun. The following month, the organization’s official website was launched, along with an Indiegogo campaign to help fund a project to create a 3D printable gun called the “Wiki Weapon.” Three weeks later, Indiegogo suspended the campaign without comment. DD continued the campaign on its own website and managed to meet its fundraising goal through PayPal and Bitcoin donations.
On December 18th, 2012, Thingiverse removed all listings for firearm and weapons-related designs. The same day, MakerBot released a statement explaining why they began enforcing restrictions on certain types of files:
“MakerBot’s focus is to empower the creative process and make things for good. MakerBot Desktop 3D Printers make innovative products, new tools, models, fashion items, works of art, and 3D things of all types. MakerBot’s Thingiverse website is designed to be the best place to get and share downloadable 3D “Things.” Thingiverse’s Terms of Service state that users agree not to use Thingiverse “to collect, upload, transmit, display, or distribute any User Content (ii) that…promotes illegal activities or contributes to the creation of weapons, illegal materials or is otherwise objectionable.” If an item has been removed, it is because it violates the Thingiverse Terms of Service."
Defense Distributed reacted by launching the website DEFCAD,[13] an alternative to Thingiverse where users can share digital designs for controversial objects like firearms and explosives. The website hosts all files believed to have been removed from Thingiverse and those submitted by users for the Wiki Weapon project.
Highlights
MineWays
Mineways is an open source 3D rendering software program developed by Eric Haines which allows Minecraft players to export their constructed worlds and print them via Shapeways.
MakerLove
MakerLove is a website where 3D print hobbyists can download and test out various adult toy designs.
R/C Transformer
Transform Robot is a 3D printed robot engineered by Brave Robotics that transforms from a remote-controlled car into a walking robot with a wifi camera, headlights and an armside dart shooter.
3D Photo Studio
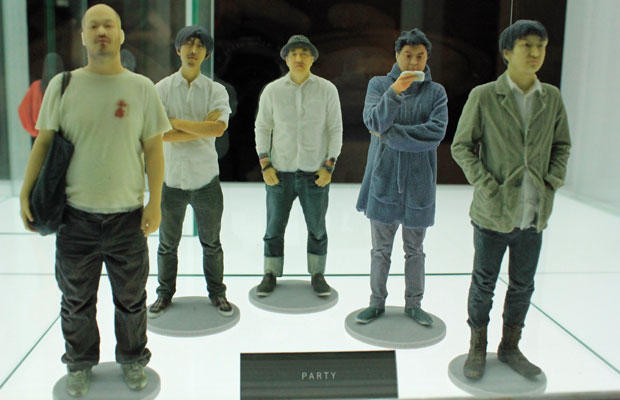
Omote 3D Shashin Kan is a 3D portrait studio located in Tokyo, Japan that uses a handheld scanner to produce a three-dimensional scale model of the model’s entire body, which is then sculpted into a intricate plastic figurine.
Human Stem Cell
In February 2013, Six scientists in the United Kingdom and Scotland successfully printed human stem cells with a “valve-based cell printer” that uses bio-inks to fabricate groups of viable stem cells that retain their ability to become any type of cell in your body.
Search Interest
External References
[2]Wikipedia – Chuck Hull
[3]Wikipedia – 3D Systems
[4]MIT– What is the 3DPTM Process?
[5]New York Times – Beam It Down From the Web, Scotty
[7]MakerBot – Hello World!
[8]MakerBot – CupCake CNC Kit
[9]Thingiverse – CupCake CNC
[10]Thingiverse – Thingiverse
[11]Makerbot – Makerbot and thingiverse at ars electronica
[12]Indiegogo – WikiWeapon
[15]3DPrinting – 3Dprinting
[16]MineWays – Real Time Rendering
[17]MakerLove – Free Sex Toy Designs for Your 3D Printer
[18]MakeZine – Best of 2012 3D Printed Objects
[19]VentureBeat – First ever: UK scientists use 3D printer to print human stem cells
[20]PetaPixel – Japanese Portrait Studio Creates Tiny 3D Sculptures Instead of 2D Photos